Firefox WebAuthn Incompatibility March 17, 2022
Gyroscope uses a CBOR library that is based on two open source libraries. The base routines follow closely Thomas Bleeker's WebAuthn Server, and the handling of the authentication data and DER routines are based on Lukas Buch's code.
When a hardware security key such as Yubi Key is enrolled, the browser sends a binary attesting data. Inside this object is another binary that is further unpacked to the raw publish keys, which are presented by the security device. After verifying the physical ownership of the hardware key, the digital publish keys are stored in the database for future logon verification.
Webkit browsers such as Chrome, Opera and Safari send a 196-byte long binary sequence for attestation. After a 53-byte header, the first two bytes, logically interpreted as a 16-bit unsigned big-endian integer, indicates the length of the actual payload.
For the same hardware key with FIDO2 disabled, Firefox uses a different layout:
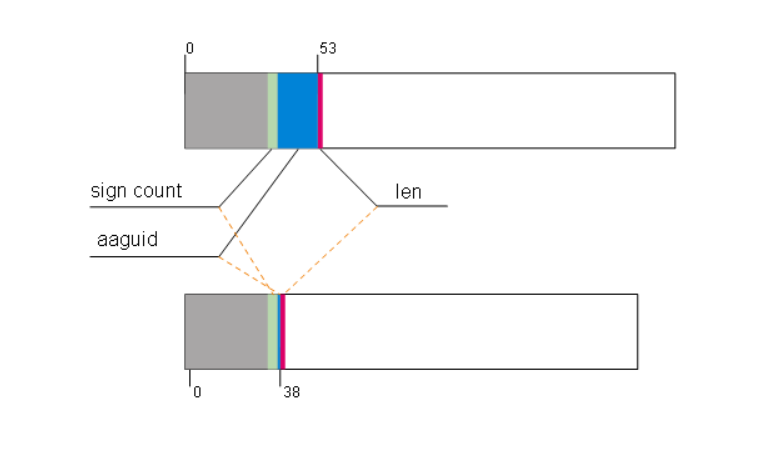
The AAGUID field should be an 128-bit field (16 bytes). Firefox gives only 1 byte.
Our patch uses the overall length of the Auth data as an heuristic indicator. If it's less than 196 bytes, the certification data is shifted by the same offset.
The patch on the WebAuthn project has also been proposed.

