Gyroscope / Framework Architecture
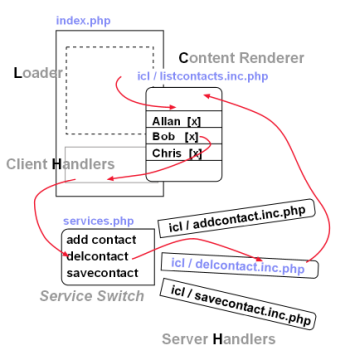
In addition to its intuitive and versatile user interface, Gyroscope is designed to be flexible and resource efficient.Gyroscope takes full advantage of the LCHH architecture. The main loader is the entry page (index.php), where the menu icons, left panel and tab view loaders are defined.
Loader
The layout and panel sizes are explicitly controlled by a window manager (viewport.js). The tab view is given the maximum possible screen real-estate.
The content in each loader is subsequently loaded through ajxpgn in the Nano AJAX Library.
In addition, Gyroscope offers higher level content loading functions:
addtab / reloadtab - load content in tabs; maintain tab order and layout
showview - loads content in the left panel; manages list order
listlookup - determines and populates the lookup loader
The above functions are further discussed in "Tab Functions",
"Building a List View", "Auto-complete Utilities" respectively.
Server-side Handlers
All the server-side handlers are routed in a switch block, which is defined in myservices.php. Note this file can take up other names, as long as the change is reflected in settings.php.
Note that the actual implementations of the handlers are stored in the icl folder. These files are included only when their corresponding handling functions are called. For example:
switch ($cmd){
case 'listtenants':
include 'icl/listtenants.inc.php';
listtenants();
break;
case 'showtenant':
include 'icl/showtenant.inc.php';
showtenant();
break;
}
case 'listtenants':
include 'icl/listtenants.inc.php';
listtenants();
break;
case 'showtenant':
include 'icl/showtenant.inc.php';
showtenant();
break;
}
The advantage of routing all the handlers through a single file is having a single point of control. The above switch structure distributes the implementation in smaller files; this effectively reduces the memory footprint.
PHP evaluates scripts by first parsing them into internal structures for further processing. This means larger scripts, or scripts that create big data objects require more memory to run. The exact memory usage can be measured by placing the following code at the end of the script:
<?php echo memory_get_usage(true); ?>
Also measure the memory usage of a blank PHP page.
You'll notice that the values are usually multiples of 262144, or 1024 x 256.
This is the least amount of memory PHP allocates for each script execution. If the script requires more memory, PHP will assign another chunk of 262144 bytes of memory, until either sufficient memory is given, or an error message "allowed memory of X bytes exhausted" is displayed.
This chunk of 262144 bytes is called a "segment". Counting segments is more convenient than counting actual bytes. It also eliminates the differences in pointer sizes in various server configurations.
Memory footprint has a direct impact on concurrency level, or the number of users the application can support at any given time. Gyroscope honors the golden standard of 1 segment memory consumption.
Client-side Handlers
A complex web application could have many features. Picture a web-based word processor, such as Google Docs. The user interface consists of many buttons; each button has a client-side handler which further communicates with a server-side handler. It would be wasteful to load all the JavaScript functions because the user typically uses a small portion of the functionality.
Gyroscope uses the ajxjs function in the Nano AJAX Library to dynamically load JavaScript handlers on demand.
Pivoting Content
The "C" in LCHH is the content, or server response that's directly injected to the loader.
In a typical Gyroscope application, the content consists of textual information, event triggers and pivoting links to other views. When the loader is populated with content, the LCHH cycle moves on.